
Glue Ear in Adults
Glue Ear (otherwise known as Otitis Media with Effusion or Serous Otitis Media) is a common medical condition which affects hearing. This can result in communication challenges at work and social difficulties.
READ MORE
Approximately 1/3 of glue ear sufferers are adults. The condition occurs when the Eustachian tube fills with fluid rather than air, usually due to a common cold. After a while the fluid can become thick and glue like affecting your hearing.
Symptoms
Dulled Hearing
Selective Hearing
Balance problems can be caused by ear conditions
Using a Louder Volume
Communication Problems
Treatment
GP
You should consult your GP if you are displaying any of the glue ear symptoms. If your GP suspects glue ear as the cause they will likely ask you to observe a “watch and wait” or “active observation” period. This happens because up to 50% of glue ear cases will spontaneously resolve without treatment.
%
50% of glue ear cases will spontaneously resolve without treatment
Audiologist
If your symptoms persist your GP will refer you to an Audiologist. Using a tympanometry test the Audiologist will diagnose glue ear. At the point of diagnosis, you will likely be asked to continue the active observation period. If the condition persists after this, they will either refer you back to your GP for an Otovent prescription or to an ENT surgeon for grommet surgery.
Watch and Wait / Active Observation

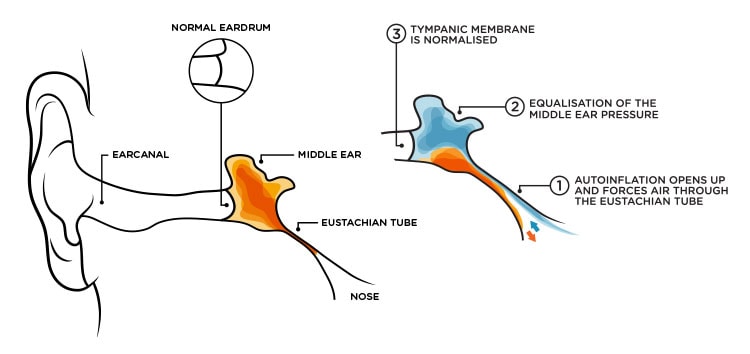
What is Otovent?
Grommet Surgery


