
Air Travel
Air travel is commonly associated with ear issues caused by pressure change when ascending and descending in the air. Otovent is an autoinflation device which equalizes pressure in the middle ear which can be useful for use during a flight. The act of inflating the specially pressurised balloon via your nose opens the eustachian tubes allowing pressure to be equalised thereby alleviating ear pain while flying.
Otovent is a fast acting, natural and non-surgical treatment as well as being compact and convenient to travel with.
Supported by clinical evidence specifically in patients when flying, using the device helps avoid ear pain during flight.

Clinically Proven
In 2004 Sven-Eric Stangerup and his team conducted a study titled “Point Prevalence of Barotitis and Its Prevention and Treatment with Nasal Balloon Inflation: A Prospective, Controlled Study“.
They concluded ‘We recommend nasal balloon autoinflation in aircraft passengers who have difficulty clearing their ears during and after flying.’
You can download the full paper and view other Otovent trials via our Clinical Data section.
Click play on the short animation to the left to learn more about Otovent Fly and how it could treat your ear discomfort or pain when you fly.
How Negative Pressure Builds Up Causing Pain in the Ears When Flying
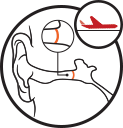
Boarding
As you board your flight middle ear pressure is normal.
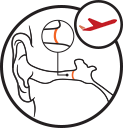
Ascent
Middle ear pressure is increased during take off resulting in a build-up of negative pressure.
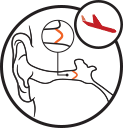
Landing
Your eardrum bulges inwards and hearing becomes almost normal as you land.
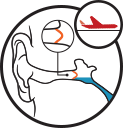
Disembarking
The eardrum remains bulged with negative pressure in the middle ear impairing hearing.
Symptoms
Barotitis is a middle ear condition which causes pain or discomfort during flight. Ear ache varies in severity between sufferers, but after flying ear pain can make scuba diving impossible, driving a challenge and in some cases the ear hurts after flight so severely that the holiday is ruined. If you have noticed any of the following symptoms you could be suffering with Barotitis:
Ear Ache
Ears Popping On Flight
Dulled Hearing
Nausea
Vertigo
Dizziness
Balance Problems

Why do my ears hurt when I fly?
Discomfort or pain in the ear during flight is caused by a build-up of negative pressure in the middle ear. During descent atmospheric pressure in the cabin rises causing a negative pressure build-up. As negative pressure increases behind the eardrum it is drawn inwards and if the pressure is not equalised it can lead to Barotitis, a very painful condition.

Is ear pressure while flying common?
Approximately 10% of adults and 20% of children develop Barotitis during flight (Stangerup et al, 2004). Barotitis is the medical name for middle ear problems caused by changing atmospheric pressures.
According to the Civil Aviation Authority, in 2016 over 270 million passengers boarded or disembarked an aircraft in UK airports, meaning many people’s ears hurt when flying.


Can I fly with glue ear?
Glue ear is a condition of the middle ear which occurs when the eustachian tubes become blocked by a thick glue like substance. This results in hearing impairment similar to the hearing experience associated with ear pain when flying. Glue Ear differs from Barotitis in that it is usually a painless condition.
You may have noticed that Otovent devices are available for the treatment of Barotitis and Glue Ear or Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. This is because the treatment methods are designed to complete identical actions – the opening of the eustachian tubes. According to the National Deaf Children’s Society (NDCS), children suffering with glue ear generally don’t experience problems flying, although your GP should always be consulted.
How To Use Otovent
Here’s how to stop your ears from popping on a plane with easy to use in-flight ear discomfort remedy Otovent Fly.
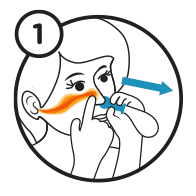
Connect
Connect the balloon to the nose piece. Hold the round part of the nose piece firmly against the right nostril with the right hand. Press the left nostril closed with the left hand.

Inflate
Inhale deeply, close the mouth and inflate the balloon until it is the size of a grapefruit by blowing through the nostril.

Repeat
Repeat the procedure with the left nostril. You will know that the treatment works if you experience a pressure increase and/or a “click” in the ear.
